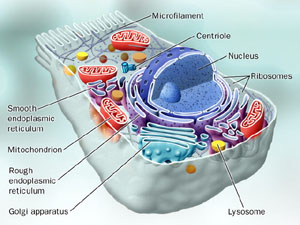
1. adhering junction Junction where a mass of anchored proteins help adjoining cells adhere.

2. adipose tissue A connective tissue having an abundance of fat-storing cells.

3. blood Fluid connective tissue of water, solutes, and formed elements (blood cells, platelets). Transports substances to and from cells, helps maintain internal environment.

4. bone tissue Of vertebrate skeleton, a tissue of osteoblast secretions hardened with minerals.

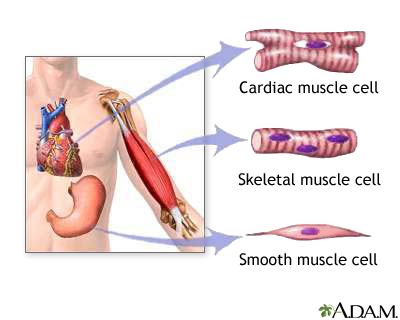
5. cardiac muscle tissue A contractile tissue that is present only in the heart wall.

6. cartilage Connective tissue with solid, pliable intercellular material that resists compression.
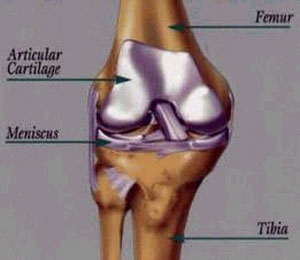
7. dense, irregular connective tissue Animal tissue with fibroblasts, many asymmetrically positioned fibers in ground substance. In skin and some capsules around organs.
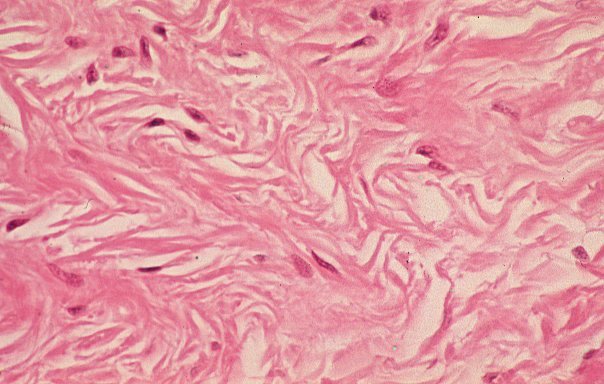
8. dense, regular connective tissue Animal tissue with rows of fibroblasts between parallel bundles of fibers. In tendons, elastic ligaments.

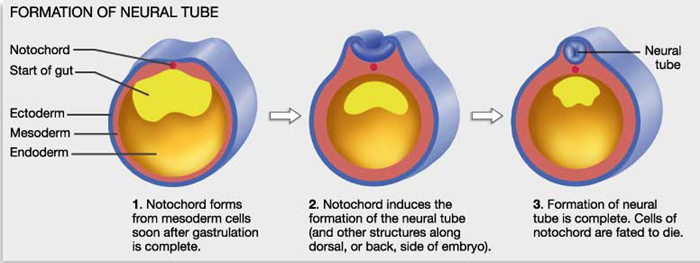
9. ectoderm The first-formed, outermost primary tissue layer of animal embryos; gives rise to nervous system tissues and integument's outer layer.
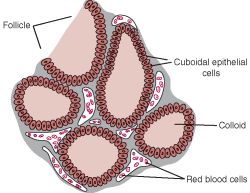
10. endocrine gland Ductless gland that secretes hormones, which the bloodstream distributes.

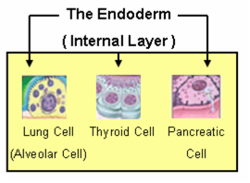
11. endoderm Inner primary tissue layer of animal embryos; source of inner gut lining and derived organs.
12. epithelium Animal tissue that covers external surfaces and lines internal cavities and tubes. One surface is free and the other rests on a basement membrane.

13. exocrine gland Glandular structure that secretes products, usually through ducts or tubes, to a free epithelial surface.

14. gap junction Cylindrical arrays of proteins in the plasma membrane that pair up as open channels for signals between adjoining cells.

15. gland cell A cell that secretes products unrelated to their own metabolism for use elsewhere.
16. homeostasis State in which physical and chemical aspects of internal environment (blood, interstitial fluid) are being maintained within ranges suitable for cell activities.

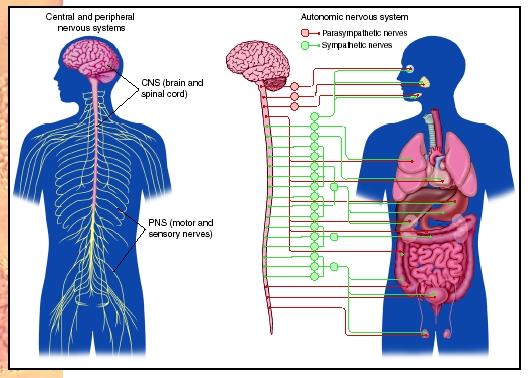
17. internal environment Blood + interstitial fluid.
18. loose connective tissue Animal tissue with fibers, fibroblasts loosely arrayed in semifluid ground substance.

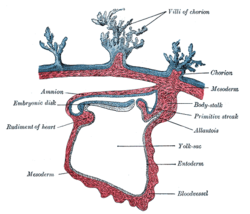
19. mesoderm Primary tissue layer of all large, complex animals; gives rise to many internal organs and part of the integument.
20. nervous tissue Connective tissue composed of neurons and often neuroglia.

21. neuroglia Collectively, cells that structurally and metabolically support neurons. They make up about half the volume of nervous tissue in vertebrates.

22. neuron Type of nerve cell; basic communication unit in most nervous systems.
23. organ Body structure with definite form and function that consists of more than one tissue.

24. organ system Organs interacting chemically, physically, or both in a common task.
25. skeletal muscle tissue Striated contractile tissue that is the functional partner of bone.

26. smooth muscle tissue Nonstriated contractile tissue found in soft internal organs.
27. tight junction Cell junction where strands of fibrous proteins oriented in parallel with a tissue's free surface collectively block leaks between the adjoining cells.

28. tissue Of multicelled organisms, a group of cells and intercellular substances that function together in one or more specialized tasks.